How Accurate Are GPS Trackers? Understanding GPS Tracking Precision
GPS tracking has transformed the way we manage and secure vehicles and assets, providing visibility into locations and movements that were previously hard to track. However, for those relying on GPS tracking systems, an essential question remains: how accurate are GPS trackers? This article explores the factors influencing GPS tracking accuracy, explains the common technology in use today, and gives insight into how you can maximize tracking precision.
Whether you're managing a fleet of vehicles or safeguarding valuable assets, understanding GPS tracking accuracy will help you make informed decisions to ensure the best results for your specific needs.
Understanding GPS Tracking Accuracy
GPS (Global Positioning System) works through a network of satellites orbiting the Earth. These satellites communicate with GPS trackers on the ground, providing location data by calculating the distance between the device and multiple satellites. By triangulating data from at least four satellites, a GPS device can determine its exact position on Earth.
The accuracy of this positioning depends on multiple factors. In ideal conditions, GPS tracking can be accurate within 3 to 10 meters. However, several elements can influence this range, from atmospheric conditions to device quality and positioning algorithms.
Key Factors Impacting GPS Tracking Precision
- Number of Satellites Connected
- The more satellites a GPS tracker connects to, the more accurate its positioning. Connecting to four or more satellites allows the tracker to triangulate a highly accurate location, reducing the margin of error.
- Atmospheric Conditions
- GPS signals travel through the Earth's atmosphere, which can slightly alter their path. Changes in temperature, humidity, and pressure can distort signals, leading to small inaccuracies in location data.
- Signal Interference
- Interference can come from several sources, including tall buildings, dense forests, and metal structures. Urban environments with skyscrapers, for instance, can reflect or block signals, leading to a "multipath effect" where signals bounce around and create location discrepancies.
- Device Quality and Calibration
- GPS devices come in a range of qualities. Higher-quality devices typically have better sensitivity and processing speed, which contribute to more precise location tracking. Calibration also plays a role; devices should be regularly updated to maintain accuracy.
- Weather Conditions
- Extreme weather conditions, such as thunderstorms, can temporarily disrupt GPS signals. Although weather rarely causes substantial inaccuracies, it can contribute to minor delays in tracking updates.
- Update Frequency and Latency
- GPS trackers with a high update frequency, sometimes called “real-time trackers,” provide location data every few seconds, which can give the impression of smoother tracking. Lower-frequency updates, while useful in saving battery, can appear less accurate because they update less often.
- Accuracy of GPS Algorithms
- GPS algorithms process raw data from satellites and translate it into location information. More advanced algorithms can better filter out inaccuracies and correct for variables like signal reflection. This is why high-end GPS systems often deliver superior accuracy compared to entry-level trackers.
GPS Tracking Technologies: Assisted GPS, Differential GPS, and Real-Time Kinematics
While standard GPS tracking is widespread, certain specialized GPS technologies can enhance tracking precision. Here's a breakdown of the most common:
- Assisted GPS (A-GPS)
- Assisted GPS, or A-GPS, uses cellular networks to assist satellite signals, especially in areas with poor satellite visibility, like dense urban centers. A-GPS speeds up the location calculation process, making it ideal for mobile devices and environments with high signal interference.
- Differential GPS (DGPS)
- Differential GPS is a technique that improves accuracy by using additional ground-based reference stations. These stations correct satellite data, making DGPS ideal for applications needing precise tracking, such as aviation or marine navigation. With DGPS, accuracy can improve to within a meter, which is exceptionally precise.
- Real-Time Kinematics (RTK)
- RTK is a specialized GPS technology that provides even higher accuracy, typically within a centimeter, by utilizing a base station that delivers real-time corrections to the GPS tracker. This system is commonly used in surveying, agriculture, and any application where exact location data is crucial.
While DGPS and RTK are highly accurate, they are also more complex and costly to implement, making them more suited to specific applications rather than everyday vehicle tracking.
How Accurate Are GPS Trackers for Fleet Management?
For businesses managing vehicle fleets, GPS accuracy is vital for efficient routing, driver monitoring, and delivery tracking. Most fleet management systems use standard GPS technology, which provides accuracy within a few meters. Here's how accuracy impacts key aspects of fleet management:
- Optimized Routes - Accurate GPS tracking allows for real-time routing adjustments, ensuring drivers follow the most efficient paths.
- Fuel Efficiency - By knowing exactly where vehicles are at all times, managers can optimize fuel usage, reducing overall costs.
- Driver Accountability - Tracking systems help enforce driver accountability, ensuring compliance with company policies and safety protocols.
- Improved ETAs - With precise tracking, estimated time of arrival (ETA) projections are more accurate, which improves customer satisfaction and operational planning.
GPS trackers used for fleet management are typically accurate enough to meet business needs, with rare deviations due to environmental or technical factors. Choosing a tracker with high update frequency and reliable connectivity will further ensure precise location reporting.
GPS Accuracy in Asset Tracking
For asset tracking, the level of required accuracy depends on the value and nature of the asset. Stationary assets, like machinery or containers, do not need highly dynamic tracking, while mobile assets, like construction equipment benefit from higher tracking precision to prevent theft and optimize logistics.
For stationary assets, GPS accuracy of 3 to 10 meters is usually more than sufficient. However, for high-value mobile assets, investing in GPS systems that offer more frequent updates and stronger signal sensitivity can enhance security and improve response times if the asset is moved unexpectedly.
GPS Accuracy for Personal Vehicles
Personal vehicle owners using GPS trackers primarily for theft recovery or employee monitoring typically find standard GPS accuracy adequate. For these purposes, an accuracy range of 3 to 10 meters suffices to provide peace of mind.
Vehicle owners in urban areas with a higher potential for signal interference may want to choose a GPS tracker that includes A-GPS or has a high sensitivity to maintain accuracy in challenging conditions.
Ways to Maximize GPS Tracking Accuracy
- Choose High-Quality Devices - Premium GPS trackers often offer better signal sensitivity, update frequency, and calibration capabilities. Look for models known for reliable performance.
- Use Trackers with Assisted GPS - A-GPS helps maintain signal strength in urban areas where traditional GPS might face challenges. A-GPS technology can significantly improve accuracy by reducing signal loss.
- Monitor Environmental Conditions - Be aware of extreme weather conditions that may impact GPS signal quality. For critical operations, you might consider redundant systems to avoid disruptions during severe weather events.
- Install the Device Properly - Proper installation is essential for optimal tracking performance. Avoid placing it near metal surfaces that could interfere with signals. Installing it under the dashboard is typically fine, as it doesn't block signals like metal would.
- Avoid Parking in Dense Structures - Parking garages and other enclosed areas made of concrete and metal can severely weaken GPS signals. If possible, avoid parking in such structures when expecting real-time tracking.
- Ensure Reliable Cellular Connectivity - A stable cellular network is crucial for accurate data transmission. Poor network coverage can delay or disrupt data flow to servers, impacting tracking accuracy.
Real-World Examples of GPS Tracking Accuracy
To better understand GPS tracking accuracy, let's consider real-world applications:
- Delivery and Logistics Companies - These companies rely on GPS tracking to streamline deliveries and provide precise ETAs. In urban areas with high traffic and signal interference, A-GPS assists in maintaining accuracy, ensuring packages reach customers on time.
- Construction Sites - Heavy machinery equipped with GPS trackers helps project managers monitor equipment locations, preventing theft and streamlining logistics. GPS accuracy enables managers to understand where each asset is located, even within large and sprawling sites.
- Agriculture - Precision agriculture benefits from GPS technology, particularly RTK, for planting, fertilization, and harvesting. Farmers can use centimeter-level accuracy to optimize crop rows and reduce waste.
- Public Transportation - Buses and trains use GPS trackers to inform passengers of real-time arrival times. In highly populated cities, accurate tracking is critical to maintain public trust and ensure reliable service.
Common Misconceptions About GPS Tracking Accuracy
- GPS Always Provides Exact Location - While GPS is generally accurate, it is not infallible. Factors like signal interference and environmental conditions can lead to slight inaccuracies.
- All GPS Trackers Offer the Same Accuracy - GPS trackers vary in quality, update frequency, and technology. High-end models provide better accuracy than entry-level devices.
- GPS Works Equally Well Everywhere - Urban areas with tall buildings and rural areas with dense forests may experience decreased accuracy. Specialized technologies like A-GPS are helpful in these situations.
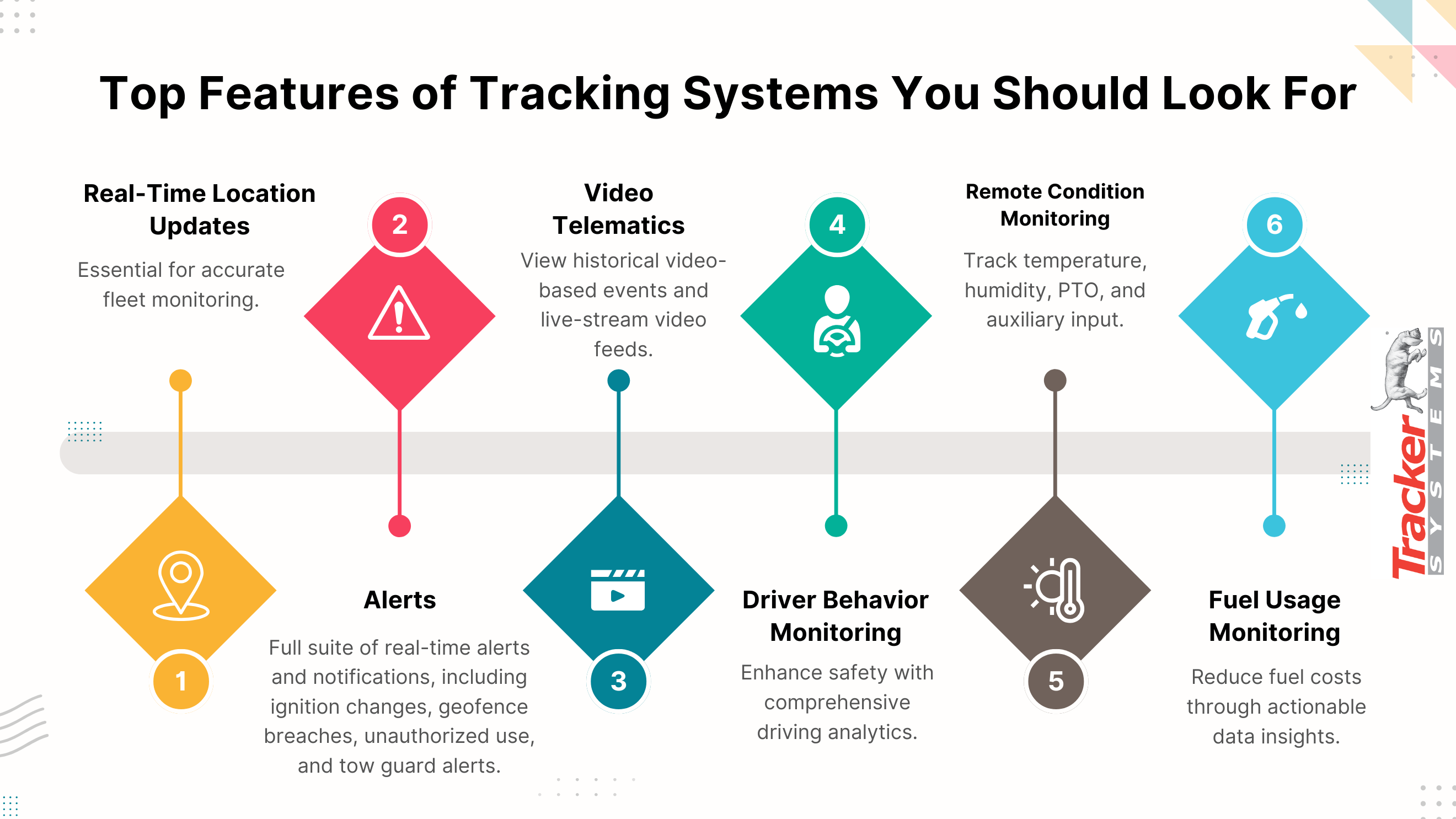
Choosing the Right GPS Tracker for Your Needs
The right GPS tracker depends on your needs for precision and reliability. Fleet managers will benefit from GPS trackers that offer frequent updates and strong connectivity, especially in areas with potential signal interference. Asset managers and personal vehicle owners should look for devices with robust tracking capabilities and theft recovery features.
When selecting a GPS tracker, consider the following factors:
- Tracking Frequency - Higher update frequency ensures smoother, more accurate tracking.
- Environmental Adaptability - Devices designed to handle interference or extreme weather provide more reliable tracking in diverse conditions.
- Battery Life and Power Source - Trackers with longer battery life or easy charging options are essential for reliability, particularly for assets or vehicles on the move.
The Future of GPS Tracking Accuracy
With ongoing advancements, GPS tracking accuracy is expected to improve significantly over time. Innovations in satellite technology are already helping address current limitations. As these technologies have evolved, GPS trackers are very reliable, ensuring that businesses and individuals can manage vehicles and assets with greater confidence.
Making the Right Choice for Reliable GPS Tracking
Understanding GPS tracking accuracy gives you the power to choose the most suitable GPS solution for your needs. With Tracker Systems, you're investing in reliable, high-quality GPS tracking devices designed to offer optimal accuracy under real-world conditions. From fleet management to asset protection, our trackers provide the security and visibility you need for confident tracking.
Invest in Accurate Tracking – Secure Your Fleet and Assets with Tracker Systems Today!
Choose Tracker Systems for precision GPS tracking that supports your business and security needs. Get in touch with our team to find the best solution for your tracking requirements and see the difference accurate tracking can make in your operations.
Recent Posts
-
Using GPS Trackers to Monitor Employee Performance
Field teams, drivers, and mobile crews are often the face of your business. They meet customers, del …Jan 5th 2026 -
GPS Trackers for Small Businesses: Boosting Security and Operations
For many small businesses, a couple of vans, a few work trucks, or a yard full of equipment represen …Dec 9th 2025 -
Understanding the Costs of GPS Trackers- A Complete Guide
Imagine this- you park your car in a busy lot, head into a store, and return only to find it missing …Dec 1st 2025



